In photovoltaics, we don't know where North is!
Or do we? But what's for sure is that we can't agree on defining an orientation (azimuth).
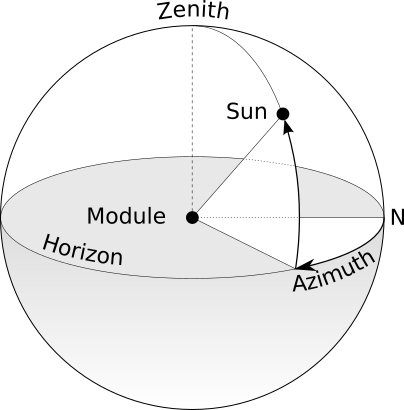
🧐 If we delve into the mathematical definition of the term, azimuth is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system.
In practical terms, the sphere doesn't matter much to us. What we want is to accurately define the orientation of the modules or the position of the sun at a given moment. So, what value should we use?
In photovoltaics, you can find everything:
PVGIS: 0° is South, and 90° is West.
HelioScope: 0° is North, and 90° is East.
Solcast, a DNV company: 0° is North, and 90° is West.
PVsyst SA: 0° is South, and 90° is West... but only in the northern hemisphere!
When market tools and literature seem to disagree... Who's right?
😊 The reality is that nobody (or everybody) is right. The important thing is to know the convention and use it correctly in each case.
Although...
🎉🎉 There is a consensus in defining North when it comes to navigation and maps (for those of us who live and move on the Earth's surface): the true/geographic North corresponds to an azimuth of 0°, increasing towards the East (90°). This is the reference used by the WMM (World Magnetic Model) and GPS and GNSS systems.
✅ This is the convention we use at ieco to define the orientation angle of surfaces (roofs and modules) as well as the position of the sun.